MRI Scan
What It Is And What To Expect
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI scan, is a special
technology that uses very powerful magnetic fields along with radio waves and a
computer to produce finely detailed pictures of the inside of a person’s body.
Unlike the faint images produced by traditional x-rays, the MRI produces
pictures of the inside of the body with a level of detail and clarity much
greater the images taken by any other imaging technology.
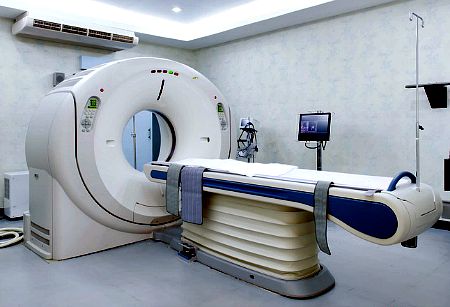
An MRI scanner is a large doughnut shaped tube that contains very powerful magnets as well as several cameras fitted inside. During an MRI scanning, a motor operated bed moves you inside the doughnut to have pictures of your body taken.
Magnetic resonance imaging scan is adjudged the safest type of detailed scanning out there because it produces none of the radiation that traditional x-rays or CT scans emit.
It can pierce through bones and reveal tissues that would otherwise be obscured, using other types of scans. For these reasons, magnetic resonance imaging scans or MRI scans are often the best method for doctors to take a look inside of your body, where the organs, blood vessels, and many abnormalities are very clearly represented.
What Can MRI Diagnose Or Show?
MRI can show or diagnose a very large number of conditions, much more than most other scans and imaging technique.
Yes. Your doctor can see many different things with an MRI scan. Part of the reason he or she can see such detailed images of the inside of the body is because the MRI take slices or cross-sections and puts them together to make 2 and 3 dimensional images.
Things that can be seen with an MRI include:
- Damaged organs that include the heart, kidneys, liver, eyes, ears, pancreas, and blood vessels, with many more images, including good images of your brain. Your doctor can see damage to the structure of any organ. Detecting damaged heart valves is an example of one good use for an MRI.
- Tumors and growths that can be benign or cancerous.
- Blood flow and blockages in organs or blood vessels.
- Torn or ruptured blood vessel linings.
- The location of a stroke caused by aneurysm or by a blockage in one of the arteries to the brain.
- Broken bones.
- Bone marrow diseases of different types.
- Torn or damaged muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
- Spinal stenosis or narrowing of the bony opening that surrounds the spinal cord for protection
- Spinal cord problems
- Bulging discs that are between the vertebrae in the back.
- Infections like collections of pus, called abscesses.
- Disease affecting the liver and other organs in the abdomen
- Causes of chronic pelvic pain like endometriosis
- MRI brain can show MS lesions (multiple sclerosis demyelination)
- MRI can show stroke
- MRI can show nerve damage of certain kind
- MRI can show spot on kidney
- MRI can show TMJ or temporomandibular joint problem
- ... and many many other problems.
This is a small sample of common uses of MRI scans. The MRI is particularly good at seeing soft tissue injuries when compared with the CT scan. Every year, new developments allow doctors to use the MRI to see different diseases and disorders within the body cavities.
Why Would My Doctor Order An MRI
Your doctor ordered an MRI scan because he noticed something on his physical examination, or another imaging test showed some abnormal finding that he could not identify.
You may have experienced any of the following symptoms:
- Weakness
- Slurred speech
- Double vision
- Blurred vision
- Drooping face
- Abdominal pain that cannot be identified
- Migraine headaches
- Chronic headache to exclude brain tumor
- Confusion
- A head trauma
- Seizures
- Heart murmur
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Persistent cough or hoarseness
- Back pain (to exclude bulging or slipped disc or nerve root compression)
- Bone or joint pain
- Hallucinations or psychosis (to exclude a physical cause)
- Sports injury (to see if you have a tendon or ligament or cartilage injury)
- Chronic sinusitis
- Multiple sclerosis (if this is suspected or to track progress of the disease)
- Chronic pelvic pain.
How Does MRI Work?
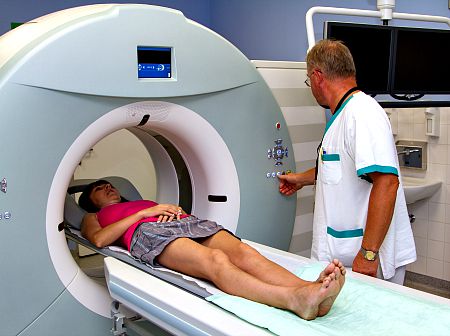 MRI Scan about to start
MRI Scan about to startHow do MRI scanners work?
Magnets play an important role in MRI technology. Large magnets are used to create powerful magnetic fields.
The magnets are arranged in a large donut-shaped tunnel that surrounds the patient, who lies still on a table in the middle of the doughnut.
- When the magnetic field is turned on it has the effect of causing all the hydrogen atoms in the body to line up in the same direction.
- Each time the magnetic field is turned off, the hydrogen atoms fall back out of alignment and release the energy that had bound them all in the same direction.
- This energy is given off in the form of radio waves, which are detected up by the MRI machine.
- The radiowaves are processed by a computer to produce images of your internal organs.
- As the MRI scan continues, the magnets inside the donut-shaped machine move around the patient to take pictures from different angles.
- The magnetic field is turned on and off at each position that can locate an organ within the body.
Depending on the number of images your doctor requires, the MRI scan usually takes from 20 to 40 minutes.
Because of the powerful magnets at work in an MRI and the several hundreds of pictures it takes in a second, an MRI machine characteristically makes a loud noise. The noise of the machine could vary from that of moving cars to birds or space ship taking off.
An MRI machine does not spine or go round you.
What Are The Risks Of MRI Scan
- MRI is a relatively very low risk test. This is because it does not use ionized radiation like those found in X-ray and Ct scan.
- If a dye or contrast is used, some people could develop life threatening allergy to the dye. If you are allergic to iodine or shellfish, you must let your doctor know
- Also, if you are diabetic and are on metformin or have kidney disease, the dye could cause more damage and you must let your doctor know. This does not mean that you cannot have the MRI scan though
- If you have pacemakers, artificial limbs, or other medical devices that are battery or electrically controlled implanted inside you, the powerful magnetic field of an MRI scan could cause such device to heat up and malfunction
- You could develop a mild fever after an MRI, if you stay inside the machine for a long time, because of the radio waves causing your body to warm up.
What Should I Do To Prepare For An MRI Scan?
MRI scan is usually a straight forward exam, as it involved taking the picture of a part of your body or your whole body, if you are doing a total body MRI.
It is non invasive, and it i snot painful.
It could be claustrophobic if you struggle with enclosed space, since it involves going into a doughnut shaped tube for 15 to 90 minutes depending on the extent of examination required and if a dye or contrast is used or nut.
To prepare for an MRI scan, it is important that you:
- Let your doctor or the MRI technician know if you are claustrophobic so that the perhaps given you some light form of sleeping medication or sedation
- Tell your doctor about any devices like pacemakers in your body.
- Tell your doctor about any prosthetic body parts or replacement parts, like hips or knees that are implanted.
- Let your doctor know in time if you have any form of metal implant - in your eye or heart or knee, ankle or anywhere else
- Let your doctor know if you are pregnant or breast feeding. MRI is save during pregnancy and breast feeding, but if you are having a dye injected into you during a scanning, it is best you wait for 24 hours for the dye to clear from your body before breast feeding your baby again. So you can prepare by expressing your breast milk that would be enough for your baby for 24 to 36 hours and keep this in the fridge before your test
- if you are having an abdominal MRI, or MRI angiogram, you should have nothing to eat for 4 to 6 hours before your scan
- You can take all your usual medications before you go for your MRI scan
- You would be required to stay very still during the time you are in the scanner
- Do not go in with jewelries or hair clips or wear clothes with zippers, snaps or underwires or metallic clips, as these could interfere with the picture taken. You might be asked to change into an hospital gown just to be sure.
The technician may give you ear plugs, because an MRI scanner is noisy.
The MRI technicians who will perform the scan will be located in a little room with glass windows, watching you while the machine is taking images. They will have a speaker and can talk with you the whole time. Some patients are able to relax and fall asleep while the scan is going on.
What Happens When My MRI Scan Is Over
When all of the images ordered by your doctor are obtained, the test is over.
The table is moved out of the MRI tunnel and you may dress and return home.
If you have had a sedative, you will have to have a friend or family member drive you home. If you have had a sedative, you may even have to be monitored for a while until you are awake.
Results of the MRI are generally not available immediately after the scan. The MRI technicians will shortly have the pictures available but it’s not their job to interpret the results for the patient.
- The radiologist will read the results in one or two days, and will report them to your doctor.
- Your doctor’s office will call you and they will tell you if there are any abnormalities, and if there are, you will probably have to return to see your doctor to plan the next step. This might include taking tissue samples (biopsy) or getting treatment.
If you had a pelvic MRI and are given hyoscine and or glucagon injection, you would need to to wait for about half an hour after your test before you can drive. This is because hyoscine could cause you to have blurred vision for a while. Be sure to clarify this with your doctor or MRI technician before leaving the scan venue.
References:
- What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) ? (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.webmd.com/a -to-z-guides/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri
- MRI: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplu/ency/article/003335.htm
- What are the Risks of an MRI scan? – MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Uses, Risks, Preparation, and Results – MedicineNet. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.medicinenet.com/mri_scanpage2.htm#3whatarei
MRI Questions And Answers
Do you have a great story, comment or perhaps questions about MRI scan or result? Share it here!
What Other Visitors Have Said
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page...
abdominal mri scan Not rated yet
Hi, I am a 37yrs old female.
I have experienced chronic lower left abdominal pain for many years now. I have been to a number of doctors, who after …



