What Is A CT Scan ?
What is a CT scan? Also called a computed tomography scan, it is a test that uses X-rays to make cross sectional images throughout your body, then puts them together through a computer program to create a detailed image of the structures inside of your body cavities.
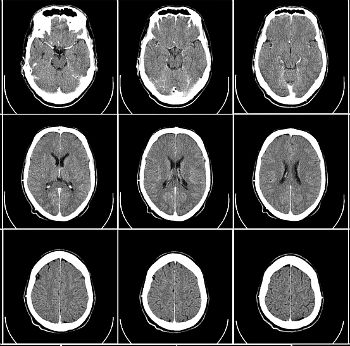
Computed tomography scan can be used to take images from all parts of your body, and the CT scan can reveal detailed pictures of your organs, blood vessels, bones, and your spinal cord.
Sometimes, a contrast dye is injected into one of your blood veins, or the contrast material may be placed in a body cavity that opens to the outside, like your rectum, to help enhance and improve the quality of image and information that can be derived from the scan.
Unlike X-rays, which mainly show pictures of bones and faint outline of soft tissues like muscles and bowels, a Ct scan shows more detail and can be used to visualize both soft tissues and bones.
Why Did My Doctor Order A CT Scan?
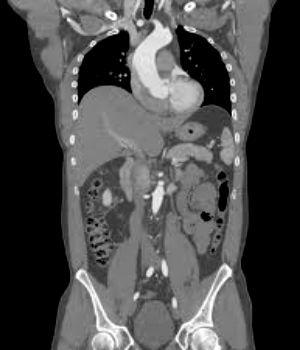 CT scan showing organs and structures in the abdomen.
CT scan showing organs and structures in the abdomen.Many times, your doctor may need a picture that is more detailed than the pictures taken by an X-ray machine or an ultrasound.
The CT scan can be used to study details in the heart, esophagus, lungs, and major blood vessels in the chest and abdomen, which include the aorta, your largest blood vessel.
A CT scan of your abdomen may find:
- Cysts, which are fluid filled structures,
- Abscesses, which are pockets of infection filled with pus.
- Areas of infection
- Enlarged lymphnodes - your doctor can even measure them with the CT scan
- Foreign object - swallowed or accidentally pushed into your body, can be located with the aid of a computed tomography scan
- If you have a tumor, that should show up on the CT scan.
- Diverticulitis, or inflammation of the small outpouchings of the intestines, can be examined.
- Inflammatory bowel disease like ulcerative colitis, a CT scan can help determine that.
- Acute appendicitis - if you have appendicitis, it will show up on a CT scan.
A CT scan of the urinary tract is called a CT urogram, and the doctor can look for
- kidney stones,
- bladder stones, or
- diseases of the kidneys,
- tumors, or
- infections.
In this type of CT, contrast dye is injected so photographs can be taken as the contrast travels through the urinary tract system.
If you seem to be having liver problems, they can often be diagnosed by CT scan, which can find
- tumors in the liver,
- bleeding, and
- other liver diseases like cirrhosis.
Sometimes, the CT scan can find the cause of jaundice, a yellow color to your skin and to the whites of your eyes.
The digestive organ called the pancreas is near the liver, and your doctor may see tumors or inflammation of the pancreas.
Your spleen may be injured in an accident, so your doctor will use a CT scan to find causes of bleeding. In some diseases the spleen may be very large and your doctor can determine its size.
If you have a tumor on your adrenal glands, or if they are enlarged, the doctor can take a look and measure them.
A CT scan of the pelvis examines the organs in the pelvis, including
- the uterus,
- ovaries, and Fallopian tubes in women, or
- the prostate gland and
- seminal vesicles in a man.
Problems with the musculoskeletal system can be identified using CT scans, including fractures or even growth problems and tumors.
If you have a biopsy of a tumor or piece of tissue inside your body, the doctor can guide the biopsy needle using the images from the CT scan. If you have a pocket of infection known as an abscess, it will have to be drained, and your doctor can do this with a needle guided by a CT.
If you have cancer, you may have CT scans periodically to see if the tumor has spread.
What To Expect When Doing A CT Scan?
The CT scan is normally done by a special doctor who reads radiographic studies, called a radiologist.
Other doctors may know how to read a CT scan, but a radiologist is specially trained, and may not miss something another doctor might now see, because radiologists have much more experience with reading a CT scan.
- Usually, you will go into a radiology suite at the hospital or in an outpatient radiology group.
- There, you be given a hospital gown, and you will be able to go into a dressing room and put the hospital gown on after you remove your other clothing.
- Take off your jewelry. You can usually leave on your underpants, but if you have a bra with metal, it may interfere with the test.
The X-ray table is attached to the CT scanner, and you will lie down on the stable before it moves into the opening of the CT scanner, which is shaped like a tube.
The table moves through the CT scanner as pictures are taken of slices of your body, and then they are reconstructed by the computer to make a picture of the entire body.
Because of radiation, the technician may sit in a booth behind glass, but she or he will be able to see you and talk to you during the test.
The test may take a total of 30 minutes to one hour, but some of that time is spent getting you situated.
How Should I Prepare For A CT Scan?
Though CT scanners are getting better every year in terms of the amount of radiation they emit when taking pictures of your body, you still need to be aware of the risk and prepare before having a scan.
- Tell your doctor if you know you are pregnant or if you think there is a chance that you may be pregnant.
- Tell your doctor if you have had studies with barium within the past four days, as it may interfere with the pictures taken by the scanner.
- Also tell your doctor if you take Pepto Bismol, and if you do, then you should for at least four days before you take have the scan.
- Also tell your doctor if you are allergic to contrast dye, medications, shellfish or if you have had asthma.
- If you have a heart condition or kidney problems, be sure to tell your doctor, and if you have had multiple myeloma, your doctor should also be aware of this.
- Finally, if you have claustrophobia, and become afraid or nervous in small spaces, ask your doctor if you may be prescribed a sedative to take before the test.
If you are having a CT scan of your abdomen, tell your doctor so he can decide whether or not to give you a laxative, and your doctor also may ask you to stop eating solid food the night before the test.
You may have a prescription for a laxative, or you may have to give yourself an enema from an enema kit. Finally, you may have to drink a lot of contrast fluid the night before the test.
What Are The Risks Of A CT Scan?
1. Radiation Risks
CT scan, like most other medical procedures or tests comes with some risk.
The greatest risk with a CT scan is that of a relatively high amount of radiation it emits into your body. To illustrate, taking a single x-ray of your chest is like being exposed to radiation from the atmosphere when you take a plane from London to Madrid.
A CT scan of your chest on the other hand, is like been exposed to 400 times the radiation you get with one single X-rays of your chest, or traveling 400 times from London to Madrid.
The good news is that, having a CT scan a few times in your lifetime should not amount to anything significant.
- Having repeat Ct scans however, can cause you to be exposed to so much radiation that this could lead to cancer or blood disease like leukemia.
- There is a small risk of cancer from some scans, and that risk is higher in children, who cannot tolerate as much radiation to their growing cells. As your doctor how much radiation exposure you can expect, if this concerns you.
- If you
have a pacemaker or a defibrillator, an insulin pump or a
neurostimulator, then your doctor needs to know so he can decide how
much the CT scan may affect the device.
The X-ray table is attached to the CT scanner, and you will lie down
on the stable before it moves into the opening of the CT scanner, which
is shaped like a tube. The table moves through the CT scanner as
pictures are taken of slices of your body, and then they are
reconstructed by the computer to make a picture of the entire body.
Because of radiation, the technician may sit in a booth behind glass,
but she or he will be able to see you and talk to you during the test.
2. Contrast Reactions
Another risk of a CT scan could comes from the dye they use, if you are having a dye test with your CT scan.
- You may feel warm from the
injection of the dye.
- You may have an allergic reaction from the
contrast eye.
- If you have kidney disease, or have diabetes and take
metformin, it may cause you a problem, and your doctor may ask you to
stop taking metformin before the test.
What To Expect After The Scan
If you have not had a sedative, you can probably go right home.
You should probably drink a lot of fluid to get rid of the radiation in the contrast material.
You may begin to eat normal solid food.
Your doctor may look at the CT exam before he talks to you that day, or he may wait for a complete reading from the radiologist, which may take one or two days. He will call you and let you know if the test is normal or abnormal.
If the test is abnormal, you may need extra tests to confirm a diagnosis, or you may need treatment for any disease that is present on the images.
References:
- Fischbach FT, Dunning MB III, eds. (2009). Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2008). FDA preliminary public health notification: Possible malfunction of electronic medical devices caused by computed tomography (CT) scanning.



