Appendicitis
Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment Options
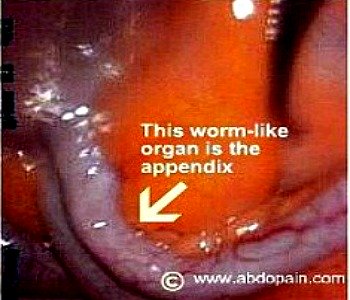
The appendix is a worm-like pouching at the junction where the small and
large intestine meets, near the cecum. About the size and shape of your
little finger, the appendix is 7 to 15cm long and 0.5 to 1.5cm wide. It is the smallest part
of the bowel and its function is not completely known.

The appendix was once thought be a vestigial organ in humans, a remnant of evolution. It is rare to find an appendix in other animals; very few species have an appendix. Current evidence suggests the appendix is indeed a very important organ that helps in the immune functions of the bowel. It is believed to house and release "good bacteria" into the bowel to aid the normal balance and function of the gut.
The appendix is usually located on the right
side of lower abdomen. In some instances (about 1 in every
10,000 people), the appendix will be on the right side of the lower abdomen.
What Is Appendicitis?
Quick Guide: How To Tell If You Are Having Appendicitis
Are you experiencing:
- Lower right abdominal pain that is made worse by coughing or moving?
- Feelings of being unwell with or without fever?
- Loss of appetite?
- Nausea?
- Pressing on your lower right abdomen about a hand's breadth to the right and below the umbilicus results in severe pain?
If these symptoms are worsening or persists for more than a day, it is best to seek medical advice as soon as possible.
Appendicitis (also called epityphilitis) is the infection or inflammation (severe irritation) of the appendix that happens when the appendix is blocked by a foreign object, stool, or cancer. It is the most common cause for emergency surgical admissions worldwide. About 70,000 operations are done in the UK yearly to remove a diseased appendix.
In the US, it is reported that 1 in every fifteen persons would come down with an inflamed appendix. The incidence of this disease is falling in the industrialized world, but sharply rising in developing countries.
Appendicitis is rare in children under the age of five. It is a condition that commonly affects those between the ages of 10 and 30 years, though it can occur at any age. It affects men more than women, but the appendix is more likely to rupture in elder adults. Women, on the other hand, are more likely to have an unnecessary operation for presumed appendicitis because of difficulties in differentiating this condition from other common causes of right lower abdominal pain in women.
Suspected appendicitis
in pregnancy occurs in less than 1% of pregnancies (1 in 500 to 1 in 635 pregnancies
per year) and is most common during the second trimester. Acute appendicitis is
even more uncommon, with 1 in 1500
pregnancies experiencing complications as a result of acute appendicitis.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
The symptoms of appendicitis are easy to spot in most people. Appendicitis typically starts as dull cramping, or central abdominal pain around the umbilicus or navel. Sufferers will usually ignore this pain, thinking it’s a minor stomachache or other temporary ailment. The early stages of appendicitis can even feel like heartburn.
Within a day or two after the initial onset of pain and discomfort, patients report their pain will shift from the belly button or umbilicus down to the right lower abdomen, and become significantly more severe. Appendicitis is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, feverishness, urinating frequently, diarrhoea (especially in children) or constipation (in adults), or dry tongue coated with a peculiar odour that doctors call fetor oris.
As appendicitis progresses the pain becomes more severe until the sufferer will find it difficult to stand upright lie flat, or to lie on their right side.
Acute appendicitis is a condition that is difficult to diagnose in babies under two years of age. At this age, the symptoms of appendicitis are unexplained crying, fever, diarrhoea and vomiting. A very high index of suspicion coupled with a careful physical examination is the best way finding out if your baby may be suffering with an inflamed appendix.
Appendicitis does not last for days and weeks. As
the pain worsens, most people will immediately seek medical attention.
Causes of Appendicitis
The exact cause of appendicitis is not known.
The appendix, like the other parts of our intestine, has a lumen. On the wall of the lumen, there are some lymph nodes. The cells on the wall of the appendix also secret mucus to keep the appendix lubricated inside.
Appendicitis occurs when the lumen of the appendix becomes blocked for whatever reason and bugs (bacteria) then multiply inside the debris formed due to the blockade and infect the wall of the appendix.
Any blockage leads to a reduction in the blood supply to the part of the appendix below the level of the obstruction. Once the blood supply of any part of the body is reduced, bacteria tend to grow fast there, and colonize the dying tissue. This is understandable because the blood provides nutrients as well as regular supply of white blood cells which act to curtail infection.
So, what are the things that could cause blockage of the lumen of the appendix and cause appendicitis? They include:
- Small lump of hard faeces ( called faecoliths)
- Parasitic worms like thread worms in children
- Benign tumour of the appendix
- Enlarged lymph nodes around or inside the appendix.
Other causes of appendicitis that has been reported include:
- Poor dietary fiber
- Virus infection causing swelling of lymph nodes inside the appendix
- Spread of infection to the appendix from a gut infection
Is appendicitis contagious? No Appendicitis is not spread by touching someone or coming in contact with an infection of any type.
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
There is no test or laboratory investigation or imaging technique that can be used to confirm the presence of an inflammation of the appendix with certainty. Diagnosis of appendicitis is mainly based on a good history or story from the patient, a thorough physical examination of the patient, and use of supportive blood test and scans, if deemed necessary.
The Alvarado Score scoring system for appendicitis is a reliable method for predicting the presence of appendicitis. The Alvarado Score adds common signs and symptoms of this condition, as well as laboratory findings to award a score of 0 to 10.
You can add up the presence or absence the symptoms and findings, and reach an Alvarado score as follows:
- Presence of pain in the right lower abdomen (scores 2)
- Pain moved from the upper abdomen to the lower right abdomen (scores 1)
- Presence of loss of appetite (scores 1)
- Feeling sick or vomiting (scores 1)
- Worsening of pain when right lower abdomen is pressed and released (scores 1)
- Presence of a temperature more than 37.3 degrees centigrade (scores 1)
- Presence of raised white blood cells (WBC) in blood test more than 10,000 (scores 2)
- Neutrophils shift to the left on blood test (scores 1)
If you have a score of 1 to 4, appendicitis is
unlikely. A score of 5-6 makes the presence of an inflamed appendix likely. A
score of 7 to 8 means the diagnosis of this condition is most likely. A score
of 9 to 10 makes this diagnosis almost certain.
Conditions That Can Cause Symptoms Similar To Appendicitis
The following are conditions that could cause symptoms similar to
appendicitis. These must be excluded to prevent unnecessary operation for a
presumed inflammation of the appendix. They include:
|
|
Treatment
Appendicitis is treated surgically, by removing the diseased appendix. This could be by the use of laparoscopy, also called keyhole surgery. This form of surgery is rapidly replacing open surgery for appendicitis. It is fast, safe and has fewer complications.
A less popular approach is to treat appendicitis using antibiotics such as metronidazole and augmentin, or cefuroxime intravenously for a few days.
Medical treatment of appendicitis should only be used if:
The operation done to treat the inflammation of the appendix is called appendicectomy or appendectomy (in the US).
You can read more about the treatment
of appendicitis here.
ICD 9 and ICD 10 Codes For Acute Appendicitis
For insurance and billing purposes, the ICD 9 code for appendicitis, depending on the details of what you hope to be coding for are:
- Acute appendicitis ICD 9 Code is 540
- Appendicitis ICD 9 code if unqualified (not stated if perforated, acute or in pregnancy) is 541
- Other diseases involving the appendix can be grouped under the ICD 9 code of 543.
References:
- (1). MRCS System Modules: Essential Revision Notes. Edited By C Parchment Smith, C Hernon. Page 376.
- Bailey & Love's Short Practice of Surgery. 23rd Edition. RCG Russell, NS Williams and CJK Bulstrode. Pages 1076 to 1092
- http://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=543883264
- http://www.icd9data.com/2014/Volume1/520-579/540-543/
- http://oxfordmedicine.com/view/10.1093/med/9780199699476.001.0001/med-9780199699476-chapter-7
Published on the 1st of June 2005 by Abdopain.com Editorial Team under causes of lower right sided abdominal pain.
Article was last reviewed on 24th April 2017.

Appendicitis Stories - Have Your Say!
Are you suffering with a right sided abdominal pain? Do you suspect that this might be due to appendicitis? Or have you had your appendix removed? What was your experience like? Share your appendicitis stories here. We would really love to hear from you!
What Other Visitors Have Said
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page...
minor could be serious?! 




Hi-so its no biggie right now...yesterday morning at around 7am I woke up and was going to sleep in a few extra minutes but I felt a little pain on the …
Please help me this is extremely urgent 




Okay so I woke up this morning about 6:00 am with a really sharp pain around my appendix... I never vomited, or had a fever today, anything. All I have …
Appendicitis 2years 4 months ago still problems bothering me 




just over 2 years ago went to hospital with servere pain was examined and told i had food poisoning sent home with various medication 2 days later was …
pain in right lower quadrant with nausea and vomiting 




pain in right lower quadrant with nausea and vomiting with movement. Area tender to touch. this has been ongoing since 4/18/11 . CT shows normal appendix. …
could this be appendicitis? 




im 15.
i had burger king on monday night, and woke up in the late night at about 3:30am with the most agonizing pain i've ever felt.
i went pee and …
confused. Not rated yet
Hi... im enelia. i had a pain in my right lower abdomen, i felt it more about 3 consecutive days. Sometimes it is really painful when i moved but sometimes …